Reducing Waste Generation: A Collective Effort for a Sustainable Future
- ierminstituteseo
- Nov 17, 2023
- 2 min read
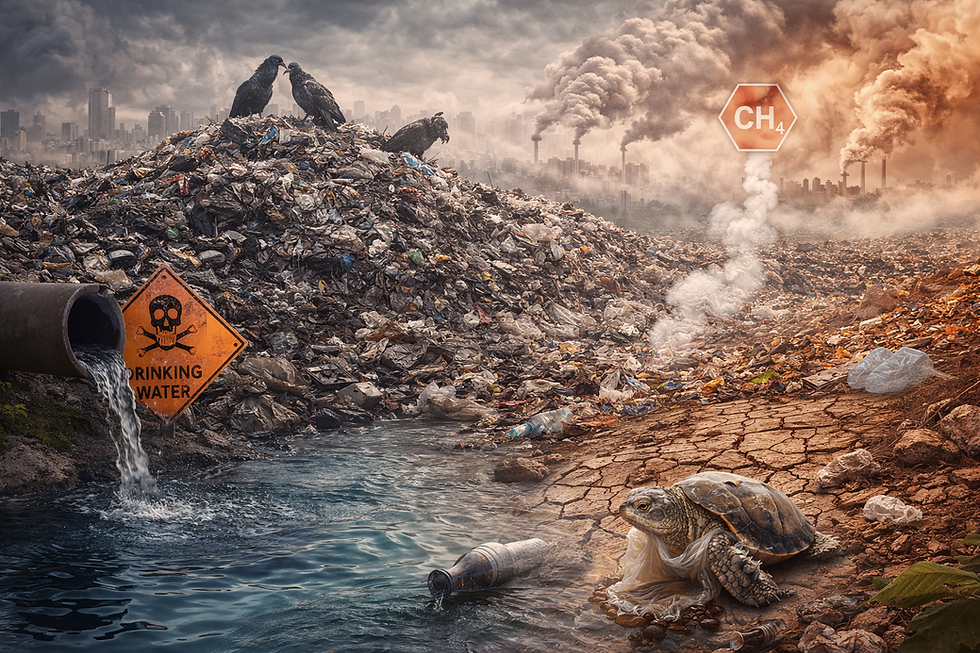
Waste generation, a byproduct of human activities, has become a significant environmental and energy resources management concern, posing challenges to global ecosystems and the health of our planet. The ever-increasing consumption of resources, coupled with unsustainable disposal practices, has led to overflowing landfills, polluted waterways, and harm to wildlife. To address this pressing issue, it is imperative to adopt strategies to reduce waste generation, promoting a circular economy and a more sustainable future.
The Impact of Waste Generation
The consequences of waste generation are far-reaching and multifaceted. Landfills, the primary destination for waste, occupy vast tracts of land, releasing harmful greenhouse gases into the atmosphere and contributing to climate change. Incineration, another waste disposal method, releases toxic pollutants into the air, posing health risks to nearby communities. Moreover, the mismanagement of waste, particularly plastic waste, leads to pollution in waterways and marine environments, endangering marine life and disrupting ecosystems.
Strategies for Waste Reduction
Tackling the problem of waste generation requires a multi-pronged approach that involves individuals, businesses, and governments.
Individual Actions:
Reduce consumption: Make conscious choices to purchase less, opting for durable, reusable items over disposable ones.
Embrace reusables: Carry reusable shopping bags, water bottles, and food containers to minimize single-use items.
Compost food scraps: Instead of throwing away food scraps, compost them to create nutrient-rich soil amendments.
Support sustainable businesses: Patronize businesses that prioritize eco-friendly practices and waste reduction initiatives.
Business Practices:
Adopt sustainable packaging: Utilize recyclable, reusable, or compostable packaging materials to minimize waste generation.
Reduce material consumption: Implement efficient production processes to minimize waste during manufacturing.
Donate or sell excess inventory: Instead of discarding unsold items, donate them to charity or sell them through online platforms.
Recycle and compost: Implement recycling and composting programs to divert Waste and Resource Management from landfills.
Government Policies:
Implement extended producer responsibility (EPR) programs: Hold producers accountable for the end-of-life management of their products, encouraging sustainable design and waste reduction.
Invest in waste management infrastructure: Develop and expand recycling facilities, composting centers, and waste-to-energy plants to effectively manage waste streams.
Promote public awareness campaigns: Educate the public about the importance of waste reduction and provide resources for implementing sustainable practices.
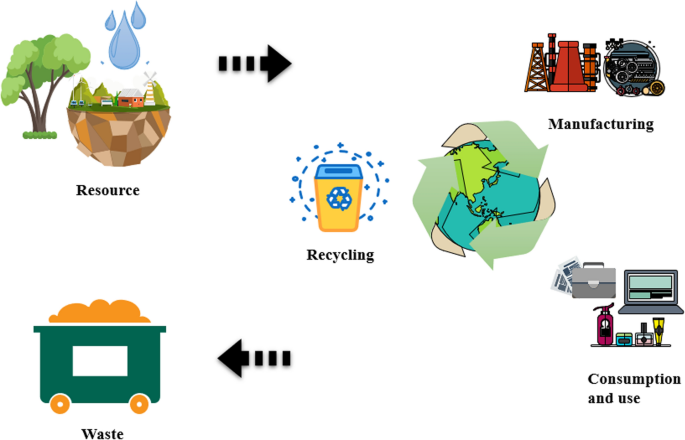
Embracing a Circular Economy
A circular economy, a paradigm shift from the traditional linear take-make-dispose model, offers a promising solution to reduce waste generation and promote sustainability. By designing products for durability, reparability, and recyclability, we can extend the life cycle of materials and minimize waste. Additionally, by adopting waste-to-resource strategies, we can transform discarded materials into valuable energy and resource management, closing the loop of resource consumption and waste generation.
Conclusion
Reducing waste generation is a collective responsibility that requires a concerted effort from individuals, businesses, and governments. By embracing sustainable practices, adopting circular economy principles, and promoting public awareness, we can significantly reduce our environmental footprint and pave the way for a more sustainable future. Let us work together to create a world where waste is not an end but a new beginning, where discarded materials become resources for innovation and a circular economy thrives.



Comments